-
General
-
Releases
-
Base Connector
-
- Beginner's Guide
- Overview
- Stations
- Datamaps
- Importing templates
- Setting conditions
- Job filter function
- How to create backups
- Running and Monitoring Jobs
- Export Job Automation
- Import/Export & copy of data map rows
- Synchronizing references that are not contained in views
- Get the preconfigured "Source data set - Template"
- Configuring categories and products
- Channel/View Tree Maintenance Active Job
- Configuring the price & stock modules
- Configuring the price/stock value ranges
- Configuring volume discounts/scale prices
- How to export prices
- How to export stock values from certain storage units
- Use of Contentserv Credentials
- Connector & Station User Limitation
- Formats
- SC::Dynamic Image Crop Preset
- Placeholders
- Show all articles ( 10 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Price Table
- Stock Table
- Sales Channel Table
- Complex Article Table
- Importing data into SAWS tables (price, stock, etc.)
- SAWSConnector Usages
- Variant Articles
- Assignment of articles to complex articles
- Searching for SC::Prices / SC::Stocks
- Searching for SC::Channels
- Setup a transformation list for CSTypes
- Context-Sensitive Product Value Export
-
- Working with placeholder in conditions
- Improve usability of SC::Tables
- Placeholder for SC::Price, SC::Channel, SC::Stock
- REST Service API for SAWS Tables (Prices, Stock, Channels & Complex Articles)
- Dataflow import of SC::Tables
- Dataflow export of SC::Tables
- The datamap summary - Creating an automated documentation
- Export images as a ZIP file
- Image export with direct access to the CONTENTSERV platform
- Image export with no access to the CONTENTSERV platform
- Image export from a third party system
- How to configure CS Dashboard
- Setup a transformation list for CSTypes
- FAQ
- Export Smart Document via Active Script and assign output to product
- Format Macros
- Controlling Connector Jobs via the REST API
- Sales Channel Maintenance via Excel Cross-Reference
- Sales Channel Inheritance Active Job
- Job Parameters & Context Parameters
- Logbook
- Fill complex article tables automatically
- Show all articles ( 7 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Owl Cloud Services
-
Owl Data Hub
-
Ursula AI
- Ursula AI
- Supported AIs
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Generate Descriptions with Ursula AI Active Job
- Populate Attributes via Ursula AI Active Job
- AI Product Tree Organizer Active Job
- Mapping Sales Channels via the Ursula AI Active Job
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
-
GenericJSON / DynamicJSON Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
GenericXML Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
SimpleExcel Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Magento Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Shopware 5 Connector
-
- Configuration Shopware
- Configuration PIM
- Shopware attribute setting
- Configuration SAWSConnector
- Station configuration
- Source data set configuration
- Configuring categories and products
- Price table configuration for Shopware
- Result in Shopware
- Subshops and the SAWSConnector Shopware
- ean
- Custom Fields (attribute)
- highlight
- purchaseSteps
- stockMin
- supplierNumber
- notification
- shippingFree
- length
- height
- width
- weight
- shippingTime
- metaKeywords
- Show all articles ( 9 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Shopware 6 Connector
-
- Tutorial Video
- First steps
- Import Shopware settings
- Export categories
- Export media files
- Export simple products
- Export multiple languages
- Export variant products
- Export product properties
- Export custom fields
- Export product cross-selling relationships
- Export prices
- Export stocks
- Export into any other Shopware field
- How to address multiple Shopware 6 websites
- How to address different Shopware 6 Sale-Channels from one Contentserv System
- Useful Links
- Sales Channel Maintenance via Excel Cross-Reference
- Show all articles ( 3 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
OXID Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Typo3 Connector
-
-
- Send value of a PIM reference
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Send value of a Channel (view) reference
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Send value of a MAM reference
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Send value of an attribute reference
- Send value of a user reference
- Loop values for user references
- Send value of a reference (deprecated)
-
- Loop values for several attributes simultaneously
- Loop values for child elements
- Loop values for CS PIM references
- Loop values for CS Channel (Views) references
- Loop values for CS MAM references
- Loop values for user references
- Loop values for SC::Prices
- Loop values for SC::Stocktable entries
- Loop values for SC::Complex products
- Loop values for a CS table
- Loop values for CS type reference
- Loop value for simple data record
- Loop values for JSON Objects
-
- Create a JSON-String (create an array)
- Format value lists
- Tree paths or values from tree elements
- Multistep formatting
- Send accesslevel of the object
- Send value of a job parameter
- Search for values in several attributes
- Format with PHP Code (deprecated)
- Format Macros
- Load data via REST Service
- AI Value Transformation Format
- AI Value Translation Format
- Store value into a Contentserv Item
- Execute a conditional format (switch-case) Format Plugin
- Load array value from the Contentserv getValues Format Plugin
- Process HTML table Format Plugin
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
Other Connectors
Filters
What is a Filter
Filters are tools or mechanisms used to refine, modify, or limit the data retrieved or processed from a larger dataset. In the context of a data management platform like the Data Hub, Filters allow you to define specific criteria to control which data is included or excluded based on conditions such as values, ranges, or patterns. The key benefits of Filters include providing data precision by retrieving exactly what you need, improving efficiency by reducing processing time and resource consumption, offering customization to tailor data access for different users or systems, and enhancing analysis by narrowing down data to the most relevant information for decision-making. Filters ensure that only the most important and actionable data is accessed or processed, streamlining workflows and improving overall data management.
A Filter in the Data Hub provides the flexibility to use a single Data Collection for multiple users or systems by applying customized data restrictions. This ensures that each user or system interacts only with the data that is relevant to their specific use case, which is particularly important when different users need access to different subsets of the same dataset. For example, you can filter data by user roles, geographic locations or specific time periods, ensuring that sensitive or unnecessary information is not exposed. This ability to dynamically adjust data access based on the caller’s needs helps maintain data security, optimize performance, and prevent data overload. Filters also make it easier to manage large and complex datasets, as they allow for fine-tuned control over how data is accessed, presented, and processed. By filtering data based on user-specific criteria, the Data Hub makes it possible to deliver a personalized and efficient data experience, even when multiple users or systems are interacting with the same underlying dataset.
Navigation to the Filter page
To get to the Filter page from the dashboard, find the Data Hub Tile and select Filter.
If the tile shown is deactivated, you do not yet have a Data Hub license. In this case, please contact sawsconnector@saws.de.
If you are not on the dashboard click the most left button in the toolbar to navigate to the dashboard page.
If you are already in the Data Hub you can use the dropdown menu in the toolbar and select the Data Collections item.
Now you should be in the Filter page which shows the Filter table list.
How does a Filter work
A Filter is a query that specifies criteria for selecting records from a Data Collection. Filters use MongoDB query syntax to define conditions that determine which records should be retrieved or updated. Filters are expressed as JSON-like objects where field names are matched against specified values or conditions.
Basic Filtering
A basic Filter selects records based on exact field-value matches. For example, to find all users with the name “John”:
{ "name": "John" }This query retrieves all records where the name field is exactly “John”.
Using Comparison Operators
A Filter provides several operators to filter documents based on conditions:
$eq(equal to)$ne(not equal to)$gt(greater than)$gte(greater than or equal to)$lt(less than)$lte(less than or equal to)
Example: Find all products with a price greater than 50:
{ "price": { "$gt": 50 } }Combining Conditions with Logical Operators
A Filter supports logical operators to combine multiple filter conditions:
$and(all conditions must be true)$or(at least one condition must be true)$not(negates a condition)$nor(none of the conditions must be true)
Example: Find all users who are either from “New York” or older than 30:
{ "$or": [ { "city": "New York" }, { "age": { "$gt": 30 } } ] }Special Query Operators
A Filter provides additional operators for more advanced filtering:
$in: Matches any value from an array.$exists: Checks if a field is present in a record.
Example: Find all users whose status is either “active” or “pending”:
{ "status": { "$in": ["active", "pending"] } }Example: Find records where the email field exists:
{ "email": { "$exists": true } }Regular Expressions
A Filter allows text pattern matching using the $regex operator.
Example: Find all users whose name starts with “A”:
{ "name": { "$regex": "^A" } }- The
^Apattern ensures that the name starts with “A”.
Example: Find all products with names containing “book” (case-insensitive):
{ "product_name": { "$regex": "book", "$options": "i" } }- The
"i"option makes the search case-insensitive.
For a more advanced tutorial on regular expressions read the Regular Expressions info guide.
Filtering Arrays
A Filter supports filter conditions for array fields.
Example: Find orders where the items array contains a product with id equal to “123”:
{ "items": { "$elemMatch": { "id": "123" } } }Example: Find users who have “admin” in their roles array:
{ "roles": { "$in": ["admin"] } }Nested Fields
A Filter supports filter conditions for nested object fields.
Example: Find users in “New York”:
{ "user.address.city": "New York" }
Creating a Filter
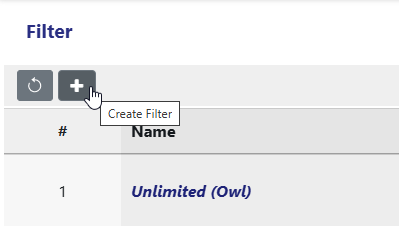
To create a new Filter, click on the Plus Button on the top left corner of the Filter table.
The editor will open where you can configure the metadata of your Filter which consists of the following:
- Name
- Data Collections
- Placeholders
- Record Filter
- Description
Name
The name should be descriptive and unique.

Data Collections
Restrict the Filter to specific Data Collections. Only Endpoints or Record Formatting References that point to one of the selected Data Collections can use this Filter. If no Data Collection is selected, this Filter can always be used. If you click the button Show Fields after you selected Data Collection you will see every field of every Data Collection in a small table which you can use as help in in the Record Filter field.

This restriction is only checked on the client and not on the server. What does this mean?
If you set a Data Collection restriction to a Filter which is already used by a Data Hub entity which does not use one of the selected Data Collections, it will still work but it will show you an empty select when you go to the editor of the Data Hub entity. Here is a short example.
We create a Filter “my-filter” without any restrictions.

Then we create a Export Endpoint which uses the Data Collection “my-collection” with our newly created “my-filter”.
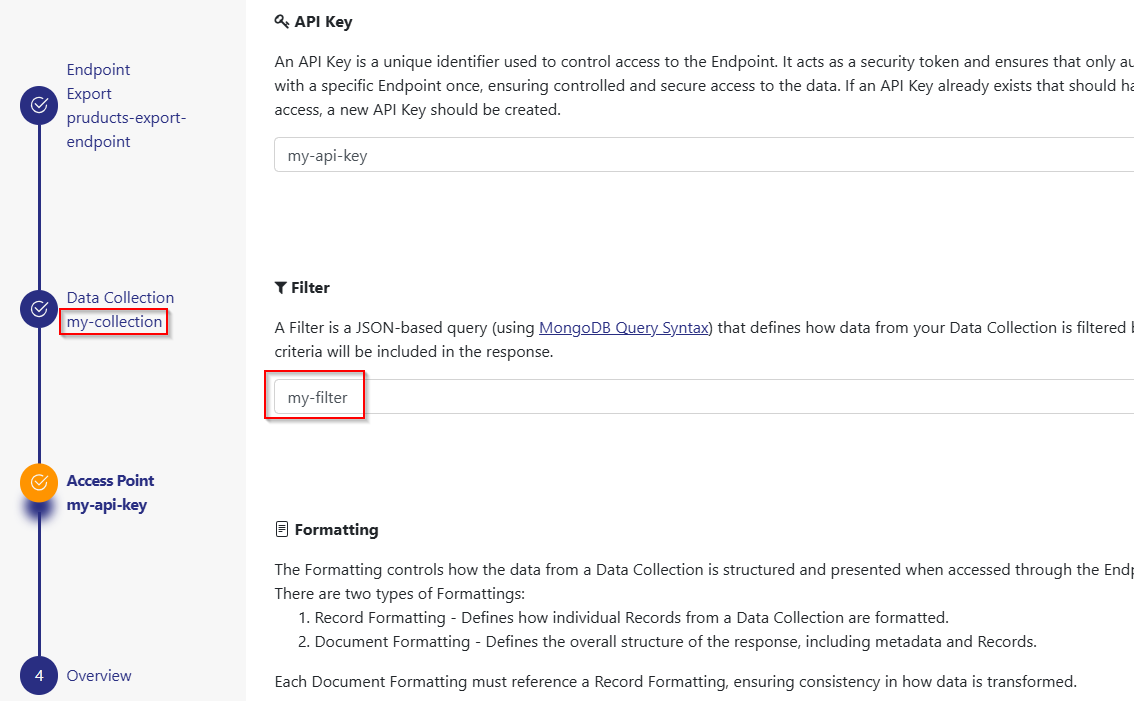
Now we restrict “my-filter” to the Data Collection “products”.
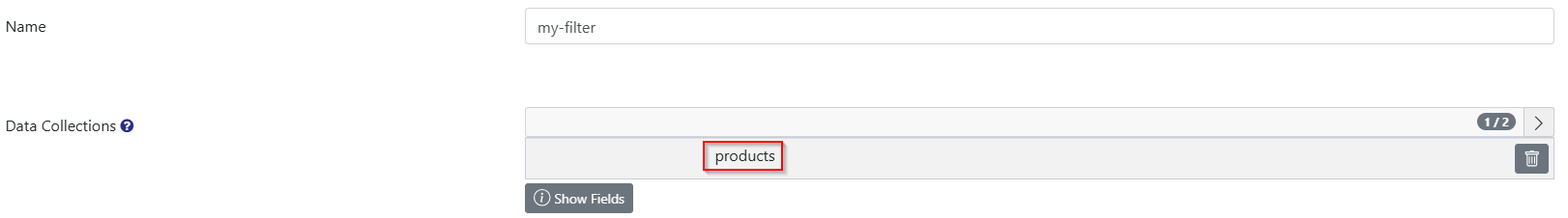
If you go back to the Access Point of your created Export Endpoint it will show you an error because “my-collection” does not fit the restriction of “products”.
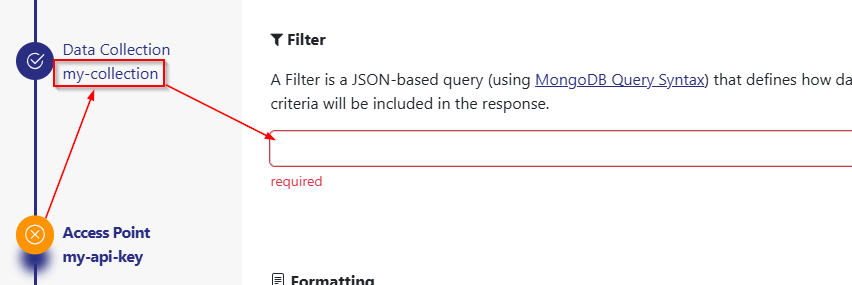
You can not save the Export Endpoint unless you change to a valid Filter. However if you use the Access Point of the Export Endpoint it will still work and apply the Filter “my-filter”.
Placeholders
In the Placeholders field you can define Variables or Placeholders which have to be filled when the Filter is referenced.
To add a Placeholder click the Plus button in the field.

Now you can define a Key, Name and a Default Value. You can use the Key in the Record Filter.
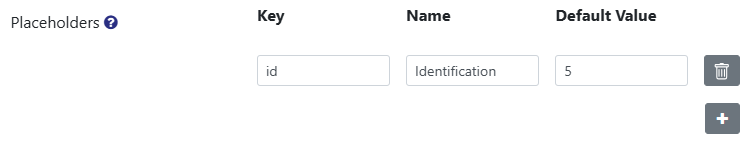
The Name will be displayed when the Filter is referenced.
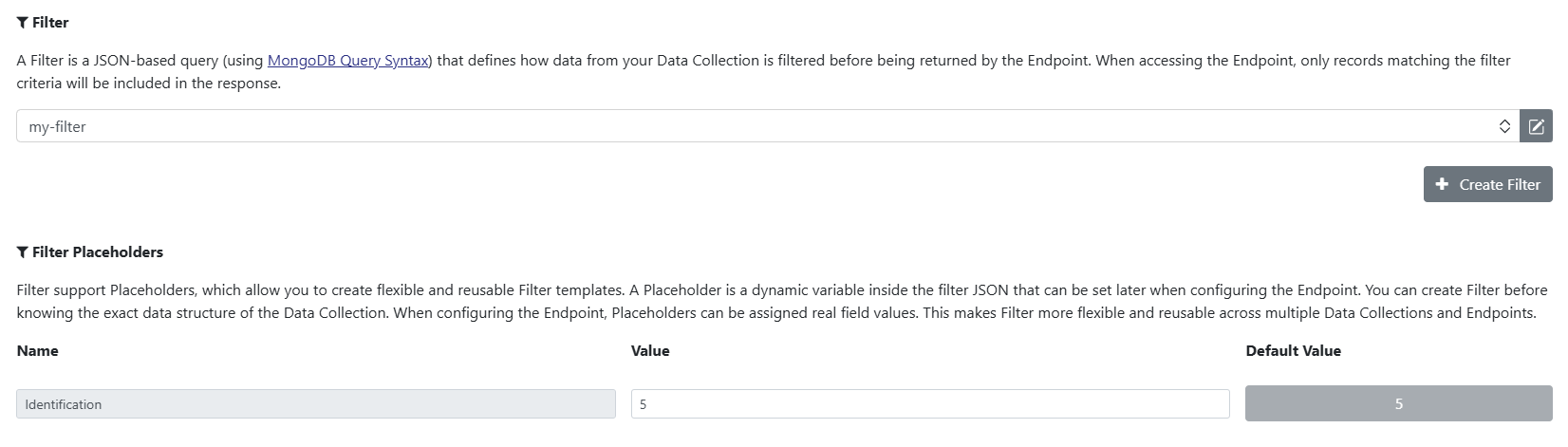
With placeholders you can define a Filter skeleton which can be finalized when you reference the Filter.
Record Filter
In the Record Filter field you can define your filter object.
You can reference Placeholders with the syntax "${placeholders.<Key>}".
{
"id": "${placeholders.id}"
}
Description
With the Description you can provide additional information and it will appear when you select the Filter somewhere as a reference.

Filter in Export Endpoints
If you access an Export Endpoint via a Access Point which has a Filter, the response will only contain records of the Data Collection which match the Filter.
Filter in Import Endpoints
If you upload a File to a Import Endpoint each record is transformed to a JSON object and then matched against the Filter and only added to the Data Collection if it matches the Filter.
Default Filter
The default Filter Unlimited (Owl) matches all records, so it doesn’t actually filter anything.
